A recent study conducted by researchers in South Korea has found that an increasing number of smokers are turning to heated tobacco products (HTPs) as an alternative to traditional cigarettes. The study, which surveyed over 4,500 adults, suggests that HTPs are becoming a popular choice due to their perceived lower health risks and the potential to help smokers quit conventional smoking. This shift highlights the evolving landscape of tobacco consumption and the growing interest in harm reduction strategies.
The study conducted by the Korea Institute for Industrial Economics and Trade revealed that a significant portion of smokers are now opting for HTPs. These products, which heat tobacco instead of burning it, are seen as a less harmful alternative to traditional cigarettes. The researchers found that 99.4% of HTP users were either former cigarette smokers or dual users, with only a small fraction being new smokers.
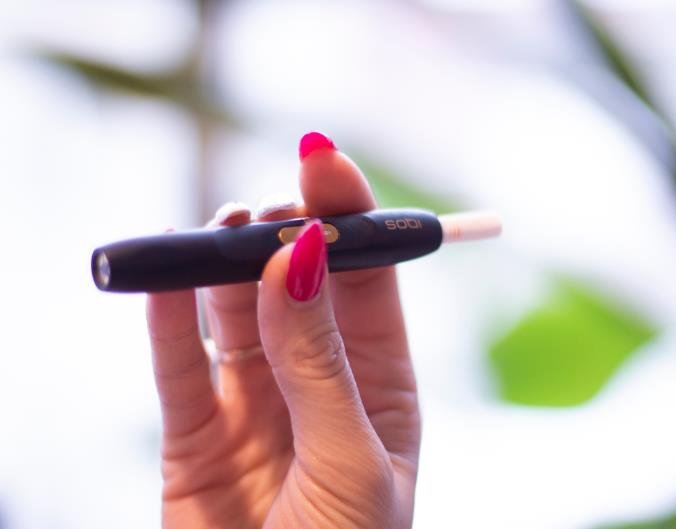

This trend is driven by the perception that HTPs reduce exposure to harmful chemicals found in cigarette smoke. Unlike traditional cigarettes, HTPs do not produce smoke, ash, or the same level of toxicants. This makes them an attractive option for smokers looking to reduce their health risks while still satisfying their nicotine cravings.
The study also noted that the availability and marketing of HTPs have played a significant role in their adoption. Companies like Philip Morris International have aggressively promoted these products, highlighting their potential benefits over conventional smoking.
Health Implications and Public Perception
The health implications of HTPs have been a topic of debate among researchers and public health officials. While HTPs are generally considered less harmful than traditional cigarettes, they are not without risks. The study emphasized that while HTPs reduce exposure to certain harmful chemicals, they still contain nicotine and other potentially harmful substances.
Public perception of HTPs has been largely positive, with many smokers viewing them as a safer alternative. However, health experts caution that more research is needed to fully understand the long-term health effects of these products. The study’s findings suggest that HTPs could play a role in harm reduction strategies, but they should not be seen as a completely risk-free option.
The researchers also highlighted the importance of regulating HTPs to ensure they are not marketed to non-smokers, particularly young people. Effective regulation can help maximize the potential benefits of HTPs while minimizing their risks.
Policy Implications and Future Research
The findings of the Korean study have significant policy implications. As more smokers turn to HTPs, policymakers need to consider how to regulate these products effectively. This includes ensuring that HTPs are not accessible to minors and that their marketing does not encourage non-smokers to start using them.
Future research is needed to explore the long-term health effects of HTPs and their potential role in smoking cessation. The study’s authors call for more comprehensive studies to understand the impact of HTPs on public health and to develop evidence-based policies that balance harm reduction with prevention.
The shift towards HTPs reflects a broader trend in tobacco consumption, where smokers are seeking alternatives that offer reduced health risks. As the landscape of tobacco use continues to evolve, ongoing research and thoughtful regulation will be crucial in addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by these new products.
Michael Brown is a seasoned journalist with a knack for uncovering compelling stories within the realm of cannabis. Through his investigative reporting and in-depth analysis, he sheds light on the regulatory challenges, market trends, and societal impacts of the burgeoning cannabis industry. Michael’s commitment to objective journalism and ethical reporting makes him a trusted voice in providing readers with balanced and informative articles about this rapidly evolving landscape.