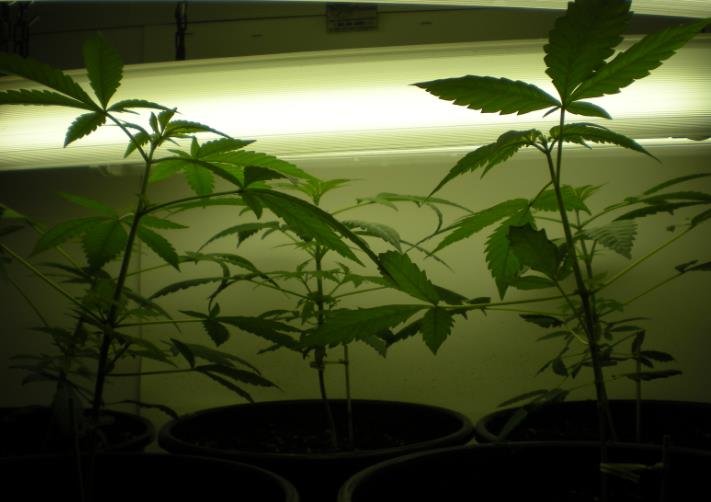
Indoor cannabis cultivation has become increasingly popular due to its ability to provide controlled growing conditions. One of the critical factors influencing the success of indoor cannabis cultivation is lighting penetration. Effective lighting ensures that all parts of the plant receive adequate light, promoting healthy growth and maximizing yield. This article explores the importance of lighting penetration in indoor cannabis cultivation, the challenges faced, and the techniques used to optimize light distribution.

Importance of Lighting Penetration
Lighting penetration is crucial for the overall health and productivity of cannabis plants. Adequate light penetration ensures that the lower branches and leaves receive sufficient light, which is essential for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, fueling their growth and development. Without proper lighting, the lower parts of the plant may not receive enough light, leading to underdeveloped buds and reduced yield.
In indoor cannabis cultivation, artificial lighting systems such as LEDs and HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) lamps are commonly used. These systems must be carefully positioned and managed to ensure even light distribution across the plant canopy. Light intensity, measured in micromoles per square meter per second (µmol/m²/s), plays a significant role in determining the effectiveness of lighting penetration. During the vegetative growth phase, cannabis plants typically require light intensities ranging from 400-600 µmol/m²/s.
The spectrum of light is also important. Full-spectrum LED lights, which mimic natural sunlight, are often preferred for indoor cultivation as they provide a balanced range of wavelengths that support various stages of plant growth. However, achieving uniform light penetration remains a challenge, requiring careful planning and adjustment of lighting systems.
Challenges in Achieving Optimal Lighting
Despite advancements in lighting technology, achieving optimal light penetration in indoor cannabis cultivation remains challenging. One of the primary issues is the limited depth of light penetration compared to natural sunlight. Sunlight can penetrate deep into the plant canopy, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive adequate light. In contrast, artificial lighting systems often struggle to achieve the same level of penetration.
Another challenge is the distribution of light. Inadequate light distribution can result in uneven growth, with some parts of the plant receiving too much light while others receive too little. This can lead to issues such as photoinhibition, where excessive light intensity damages the photosynthetic apparatus, and light starvation, where insufficient light impairs growth and development.
Thermal management is also a critical factor. High-intensity lighting systems can generate significant heat, which must be managed to prevent damage to the plants. Proper ventilation and cooling systems are essential to maintain an optimal growing environment. Additionally, the positioning of lights must be adjusted regularly to accommodate the growth of the plants and ensure consistent light penetration.
Techniques to Enhance Light Penetration
Several techniques can be employed to enhance light penetration in indoor cannabis cultivation. One effective method is the use of light movers, which help distribute light more evenly across the plant canopy. Light movers can be programmed to move lights back and forth, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive adequate light exposure.
Another technique is the strategic positioning of lights. Placing lights closer to the plant canopy, typically around 12-18 inches, can improve light penetration and bud production. However, care must be taken to avoid excessive light intensity that can cause photoinhibition.
Pruning and training techniques, such as topping and low-stress training (LST), can also improve light penetration. These methods involve trimming and bending the plants to create a more open canopy structure, allowing light to reach the lower branches and leaves. This not only enhances light penetration but also promotes better air circulation, reducing the risk of mold and mildew.
In conclusion, lighting penetration is a critical factor in indoor cannabis cultivation that directly impacts plant health and yield. By understanding the challenges and employing effective techniques, growers can optimize light distribution and create a thriving indoor growing environment.
Michael Brown is a seasoned journalist with a knack for uncovering compelling stories within the realm of cannabis. Through his investigative reporting and in-depth analysis, he sheds light on the regulatory challenges, market trends, and societal impacts of the burgeoning cannabis industry. Michael’s commitment to objective journalism and ethical reporting makes him a trusted voice in providing readers with balanced and informative articles about this rapidly evolving landscape.